| 1.B.27 The Helicobacter Outer Membrane Porin (Hop) Family
The Hop family consists of 31 outer membrane proteins in Helicobacter pylori. Five such proteins, HopA-HopE have been shown to function as porins both in bacterial outer membranes and in reconstituted planar bilayer membranes. The HopE protein appears to form a β-barrel with 16 transmembrane amphipathic β-strands. It is the smallest of the characterized Hop family members, but it forms the largest channels with a single channel conductance of 1.5 nS in 1M KCl (Bina et al. 2000).
Helicobacter pylori attaches to gastric tissue through members of a paralogous family of 'Helicobacter outer membrane proteins' (Hops), including adhesins BabA, SabA, HopQ, LabA and HopZ. Hops share a conserved 25 kDa C-terminal region that is thought to form an autotransporter-like transmembrane domain. Hops contain a non-continuous transmembrane domain, composed of seven predicted beta-strands at the C-terminus and one at the N-terminus (Coppens et al. 2018). Folding and outer membrane localization of the C-terminal beta-domain depends on a predicted transmembrane beta-strand within the first 16 N-terminal residues. The N-terminus resides in the periplasm, and the crystal and small angle X-ray scattering structures for the SabA extracellular domain reveal a conserved coiled-coil stem domain that connects to transmembrane beta-strands 1 and 2. Thus, Hop adhesins represent a novel outer membrane protein topology encompassing an OmpA-like 8-stranded beta-barrel that is interrupted by a 15 - 108 kDa domain inserted inside the first extracellular loop. The insertion of large, folded domains in extracellular loops is unprecedented in bacterial outer membrane proteins (Coppens et al. 2018). It is possible that these proteins are autotransporters.
The generalized transport reaction catalyzed by Hop family porins is:
solute (out) 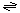 solute (periplasm) solute (periplasm)
|
| References: |
Bina, J., M. Bains, and R.E. Hancock. (2000). Functional expression in Escherichia coli and membrane topology of porin HopE, a member of a large family of conserved proteins in Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 182: 2370-2375.
|
Coppens, F., G. Castaldo, A. Debraekeleer, S. Subedi, K. Moonens, A. Lo, and H. Remaut. (2018). Hop-family Helicobacter outer membrane adhesins form a novel class of Type 5-like secretion proteins with an interrupted β-barrel domain. Mol. Microbiol. 110: 33-46.
|
de Jonge, R., R.G. Pot, R.J. Loffeld, A.H. van Vliet, E.J. Kuipers, and J.G. Kusters. (2004). The functional status of the Helicobacter pylori sabB adhesin gene as a putative marker for disease outcome. Helicobacter 9: 158-164.
|
Kennemann, L., B. Brenneke, S. Andres, L. Engstrand, T.F. Meyer, T. Aebischer, C. Josenhans, and S. Suerbaum. (2012). In vivo sequence variation in HopZ, a phase-variable outer membrane protein of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 80: 4364-4373.
|
Lienlaf, M., J.P. Morales, M.I. Díaz, R. Díaz, E. Bruce, F. Siegel, G. León, P.R. Harris, and A. Venegas. (2010). Helicobacter pylori HopE and HopV porins present scarce expression among clinical isolates. World J Gastroenterol 16: 320-329.
|
Paraskevopoulou, V., V.G. Artiaga, R. Rowlinson, G.S. Winkler, P. Gellert, S. Stolnik, R. Overman, and F.H. Falcone. (2019). Introduction of a C-terminal hexa-lysine tag increases thermal stability of the LacDiNac binding adhesin (LabA) exodomain from Helicobacter pylori. Protein Expr Purif 163: 105446.
|
Peck, B., M. Ortkamp, K.D. Diehl, E. Hundt, and B. Knapp. (1999). Conservation, localization and expression of HopZ, a protein involved in adhesion of Helicobacter pylori. Nucleic Acids Res 27: 3325-3333.
|
Sedarat, Z. and A.W. Taylor-Robinson. (2024). Outer Membrane Proteins and Virulence Factors: Potential Targets for Novel Therapies and Vaccines. Pathogens 13:.
|
Tomb, J.F., O. White, A.R. Kerlavage, R.A. Clayton, G.G. Sutton, R.D. Fleischmann, K.A. Ketchum, H.P. Klenk, S. Gill, B.A. Dougherty, K. Nelson, J. Quackenbush, L. Zhou, E.F. Kirkness, S. Peterson, B. Loftus, D. Richardson, R. Dodson, H.G. Khalak, A. Glodek, K. McKenney, L.M. Fitzegerald, N. Lee, M.D. Adams, E.K. Hickey, D.E. Berg, J.D. Gocayne, T.R. Utterback, J.D. Peterson, J.M. Kelley, M.D. Cotton, J.M. Weidman, C. Fujii, C. Bowman, L. Watthey, E. Wallin, W.S. Hayes, M. Borodovsky, P.D. Karp, H.O. Smith, C.M. Fraser, and J.C. Venter. (1997). The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 388: 539-547.
|
| Examples: |
| TC# | Name | Organismal Type | Example |
| 1.B.27.1.1 | large channel porin, HopE (Lienlaf et al. 2010). | Proteobacteria | HopE of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.10 | SabA adhesion domain-containing protein of 711 aas. The extracellular domain is a conserved coiled-coil stem domain that connects to transmembrane beta-strands 1 and 2 (Coppens et al. 2018). SabA is 96% identical to LabA of the same organism (Paraskevopoulou et al. 2019). It is one of many porins found in Helicobacter pylori (Sedarat and Taylor-Robinson 2024). | | SabA of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.11 | HopQ of 632 aas | | HopQ of Helicobacter pylori (Campylobacter pylori) |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.12 | HopZ of 666 aas | | HopZ of Helicobacter pylori (Campylobacter pylori) |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.13 | Outer membrane porin, AlpA, of 517 aas with 1 N-terminal TMS. It is also indicated as an adhesin. | | AlpA of Heilcobacter pylori
|
| |
| 1.B.27.1.14 | Outer membrane porin, BabB of 135 aas and 1 N-terminal TMS (Sedarat and Taylor-Robinson 2024). | | BabB of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.2 |
Putative outer membrane porin, HopK | ε-Proteobacteria | HopK of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.3 | Putative porin, HorG | ε-Proteobacteria | HorG of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.4 | Putative porin, HomA | ε-Proteobacteria | HomA of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.5 | Outer membrane porin/adhesin, BabA (HopZ) (Peck et al. 1999). Exhibits phase variation (Kennemann et al. 2012). | Proteobacteria | BabA of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.6 | Outer membrane porin/adhesion, SabB or HopO of 623 aas (de Jonge et al. 2004). | Proteobacteria | HopO of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.7 | Outer membrane porin, HopF of 485 aas | Proteobacteria | HopF of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.8 | Outer membrane porin, HopV, of 248 aas (Lienlaf et al. 2010). | Proteobacteria | HopV of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| 1.B.27.1.9 | Putative proin, HopK, of 284 aas | Proteobacteria | HopK of Helicobacter cetorum |
| |
| Examples: |
| TC# | Name | Organismal Type | Example |
| 1.B.27.2.1 | Putative porin (based on homology) of 222 aas, Hop-2. | Proteobacteria | hop-2 of Helicobacter hepaticus |
| |
| 1.B.27.2.2 | Putative porin (based on homology) of 209 aas, Omp30. | Proteobacteria | Omp30 of Helicobacter hepaticus |
| |
| 1.B.27.2.3 | Putative porin of 284 aas. | Proteobacteria | Porin of Helicobacter pylori |
| |
| Examples: |
| TC# | Name | Organismal Type | Example |
| 1.B.27.3.1 | Putative porin of 213 aas | | Porin of Flavobacteria bacterium BAL38 |
| |
| 1.B.27.3.2 | OmpA family protein of 417 aas and 1 N-terminal TMS. | | OmpA-like protein of Flavobacterium sp. Root420 |
| |
 solute (periplasm)
solute (periplasm)