| 1.B.31 The Campylobacter jejuni Major Outer Membrane Porin (MomP) Family Campylobacter jejuni MomP is a trimeric, β -sheet-type porin of 424 aas that packs with different lattice types when reconstituted with lipids. The protein can exist as the native trimer or as a stable monomer, depending in the concentration of sodium dodecyl sulfate. It serves several physiological functions: (1) in the structural organization of the outer membrane, (2) as an adhesin, and (3) as a porin. The monomeric and trimeric porins exhibit similar single channel conductances with the same cation selectivities and the same sensitivities to voltage when reconstituted in an artificial lipid bilayer. A second homologue of MomP with 88% identity to the first one has been sequenced (gbAL139077). The transport reaction catalyzed by the C. jejuni MomP is: solutes (out) 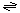 solutes (periplasm) solutes (periplasm)
|
This family belongs to the Outer Membrane Pore-forming Protein I (OMPP-I) Superfamily .
|
| References: |
Bolla, J.M., N. Saint, G. Labesse, J.M. Pagès, and C. Dumas. (2004). Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic studies of MOMP (major outer membrane protein) from Campylobacter jejuni. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60: 2349-2351.
|
Dé, E., M. Jullien, G. Labesse, J.M. Pagès, G. Molle, and J.M. Bolla. (2000). MOMP (major outer membrane protein) of Campylobacter jejuni; a versatile pore-forming protein. FEBS Lett. 469: 93-97.
|
Dhanasekar, N.N., S. Aliouane, M. Winterhalter, J.M. Pagès, and J.M. Bolla. (2017). Peptide translocation across MOMP, the major outer membrane channel from Campylobacter jejuni. Biochem Biophys Rep 11: 79-83.
|
Mohan, V. and I. Habib. (2019). Multilocus sequence typing (MLST), porA and flaA typing of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from cats attending a veterinary clinic. BMC Res Notes 12: 76.
|
Vanmarsenille, C., I. Díaz Del Olmo, J. Elseviers, G. Hassanzadeh Ghassabeh, K. Moonens, D. Vertommen, A. Martel, F. Haesebrouck, F. Pasmans, J.P. Hernalsteens, and H. De Greve. (2017). Nanobodies targeting conserved epitopes on the major outer membrane protein of Campylobacter as potential tools for control of Campylobacter colonization. Vet Res 48: 86.
|
Zhuang, J., A. Engel, J-M. Pages, and J.M. Bolla (1997). The Campylobacter jejuni porin trimers pack into different lattice types when reconstituted in the presence of lipid. Eur. J. Biochem. 244: 575-579.
|
| Examples: |
| TC# | Name | Organismal Type | Example |
| 1.B.31.1.1 | The major MomP or PorA porin can exist as functional monomers and trimers; both exhibit ion conduction activity as well as the same cationic selectivity and sensitivity to low voltage (Dé et al. 2000; Bolla et al. 2004). It can transport polyarginine peptides (Dhanasekar et al. 2017). Nanobodies against MomP restrict Campylobacter colonization (Vanmarsenille et al. 2017). Healthy cats can carry C. jejuni of limited genetic diversity (Mohan and Habib 2019). | Proteobacteria | MomP of Campylobacter jejuni |
| |
| 1.B.31.1.2 | Putative porin | ε-Proteobacteria | Putative porin of Wolinella succinogenes |
| |
| 1.B.31.1.3 | Putative porin | ε-Proteobacteria | Putative porin of Helicobacter canadensis |
| |
| 1.B.31.1.4 | Putative porin | ε-Proteobacteria | Putative porin of Arcobacter bulzleri |
| |
| 1.B.31.1.5 | Putative porin | ε-Probeobacteria | Putative porin of Caminibacter mediatlanticus |
| |
| 1.B.31.1.6 | Putative porin of 392 aas | Proteobacteria | Putative porin of Campylobacter rectus |
| |
| 1.B.31.1.7 | PorA1 of 425 aas | Proteobacteria | PorinA1 of Campylobacter lari |
| |
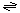 solutes (periplasm)
solutes (periplasm)