1.B.16 The Short Chain Amide and Urea Porin (SAP) Family
The SAP family includes an outer membrane porin (FmdC) found in the bacterium Methylophilus methylotrophus. Its synthesis is inducible by short chain amides and urea, and the protein presumably transports these molecules across the outer membrane when these nitrogen sources are present at low concentrations. The protein is 390 amino acyl residues in length and consists largely of β-structure. It has only one homologue (25% identity), a protein found in Aquifex aeolicus (385 aas).
The generalized transport reaction catalyzed by FmdC is:
Amides (out) 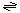 Amides (periplasm)
Amides (periplasm)
This family belongs to the: Outer Membrane Pore-forming Protein I (OMPP-I) Superfamily .
References associated with 1.B.16 family:
Jahan, M.I., P. Juengwiwattanakitti, Y. Izu, R. Tobe, T. Imai, and H. Mihara. (2019). Selenite uptake by outer membrane porin ExtI and its involvement in the subcellular localization of rhodanese-like lipoprotein ExtH in Geobacter sulfurreducens. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 516: 474-479. 31229265
Jahan, M.I., R. Tobe, and H. Mihara. (2018). Characterization of a Novel Porin-Like Protein, ExtI, from Geobacter sulfurreducens and Its Implication in the Reduction of Selenite and Tellurite. Int J Mol Sci 19:. 29534491
Mills, J., N.R. Wyborn, J.A. Greenwood, S.G. Williams, and C.W. Jones. (1997). An outer-membrane porin inducible by short-chain amides and urea in the methylotrophic bacterium Methylophilus methylotrophus. Microbiology 143: 2373-2379. 9245819